武汉华美生物工程有限公司CUSABIO®品牌商
15 年
手机商铺
- NaN
- 0
- 0
- 2
- 2
推荐产品
公司新闻/正文
“细胞胶水”变抗癌武器?Claudin家族正在改写实体瘤治疗规则
645 人阅读发布时间:2026-01-30 14:48
作为细胞紧密连接的核心架构蛋白,Claudin家族不仅在维持组织屏障完整性与选择性通透中发挥基础性生理功能,更在多种疾病发生与发展过程中扮演关键角色。该家族包含27个成员,其表达谱与功能在不同组织中高度特异,涉及肿瘤、代谢性疾病、感染与炎症等多种病理过程。近年来,随着对Claudin家族功能机制的深入研究,其中多个成员已成为疾病诊断与靶向治疗的重要研究对象。
尤其在肿瘤领域,Claudin家族成员的异常表达与多种实体瘤的发生、侵袭及预后密切相关。以CLDN18.2为代表的成员,凭借其在胃癌、胰腺癌等恶性肿瘤中的特异性高表达,迅速成为靶向药物研发的热点。2025年ESMO大会上,多款靶向CLDN18.2的国产ADC首次公布临床数据,展现出良好的抗肿瘤活性与可控的安全性,进一步验证了该家族蛋白作为治疗靶点的转化潜力。
随着Claudin家族在疾病机制与靶向治疗中的作用不断被揭示,相应的研究工具与试剂支持也显得尤为关键。CUSABIO致力于提供覆盖全家族的高品质蛋白、抗体及检测试剂盒,持续支持科研与临床转化探索,推动这一重要蛋白家族从基础研究走向精准医疗的广阔未来。
1. Claudin蛋白家族概览
Claudin蛋白是一类四次跨膜蛋白,其N端和C端均位于细胞质内。它们通过细胞外环区与相邻细胞膜上的Claudin分子相互作用,形成线性的纤维状结构,即“紧密连接链(Claudin strands)”。这些连接链紧密融合相邻细胞的质膜,有效封闭了细胞间的间隙,从而构成了物理屏障的骨架。
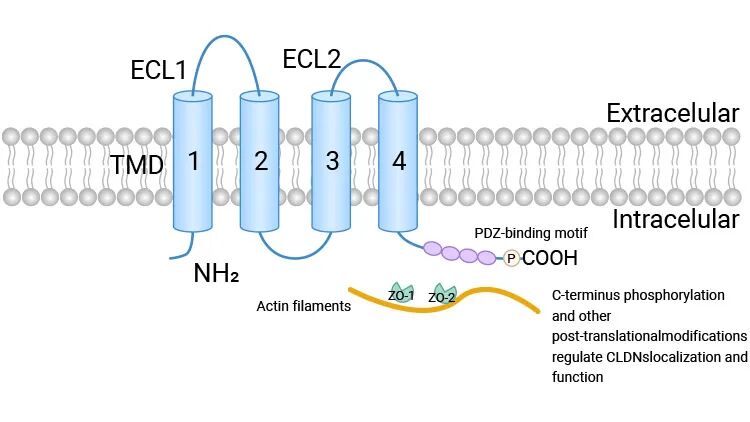
Claudin蛋白结构示意图 [1]
目前,人类基因组中已鉴定出至少27个Claudin家族成员(Claudin-1至Claudin-27)。尽管同属一家族,但不同Claudin蛋白在组织分布、表达水平及其在紧密连接中的具体功能上存在显著差异,使其能够适应不同组织的生理需求。
Claudin蛋白的核心功能主要体现在两方面:
Claudin蛋白通过形成连续的细胞间"密封"结构,有效阻止水溶性分子、离子和微生物在细胞间隙的自由渗透。这对于维护各器官内部环境的独立性和稳定性至关重要,例如肠道屏障阻止有害物质进入循环系统,血脑屏障则保护中枢神经系统免受血液中潜在有害物质的侵扰。
除了阻隔作用,特定的Claudin蛋白还能形成纳米级的"旁细胞水性孔道(paracellular pores)",介导离子和小分子在细胞间隙的选择性转运。Claudin成员的种类和组合决定了这些孔道的电荷选择性和大小选择性,从而实现对钙、镁、钠、氯等离子的精确重吸收和分泌,对维持机体的水盐平衡和物质代谢具有关键作用。
正是由于Claudin蛋白在构建和调控生理屏障中的核心作用,其功能或表达的异常与多种疾病的发生发展密切相关。因此,Claudin蛋白家族已成为生物医学研究的重要焦点,被广泛关注。
研究表明,Claudin蛋白的失调与多种人类疾病(如癌症、炎症性疾病、代谢疾病和感染)存在关联。鉴于其在病理生理过程中的关键地位,Claudin蛋白不仅为深入理解疾病机制提供了重要线索,也展现出作为诊断标志物和潜在药物靶点的巨大潜力。针对Claudin蛋白的功能调控有望为多种顽固性疾病的治疗带来创新策略。
2. Claudin 家族的生理分布及其在疾病中的作用
2.1Claudin蛋白在组织/器官中的表达
Claudin 蛋白在不同组织和器官中的表达模式存在显著差异。深入理解这些特异性的表达模式对于研究者选择合适的阳性对照、准确解读实验结果以及探索 Claudin 蛋白的生理功能至关重要。
表 Claudin 蛋白在主要人体组织/器官中的表达特征
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
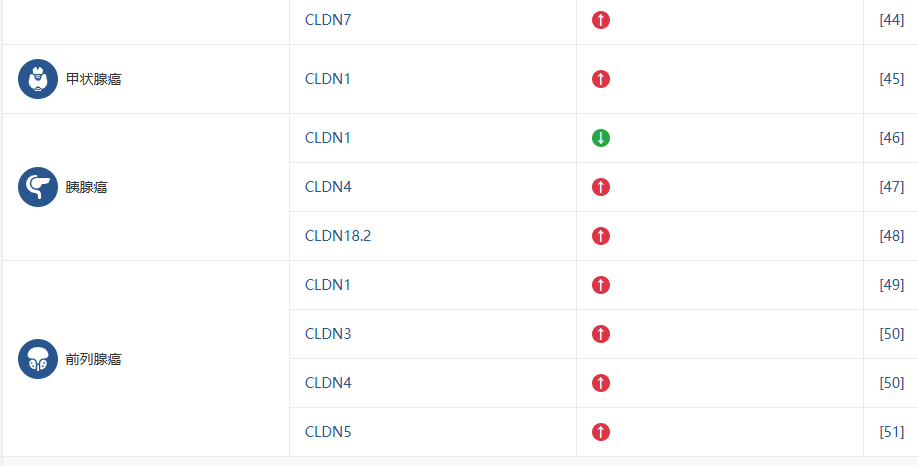
2.2 Claudin家族与疾病研究
Claudin 家族的不同成员被证实与多种疾病的发生发展密切相关,这使得它们成为极具价值的生物标志物和潜在的治疗靶点。下表总结了 Claudin 成员与主要疾病的关联,旨在帮助您快速识别与您研究方向相关的靶点。
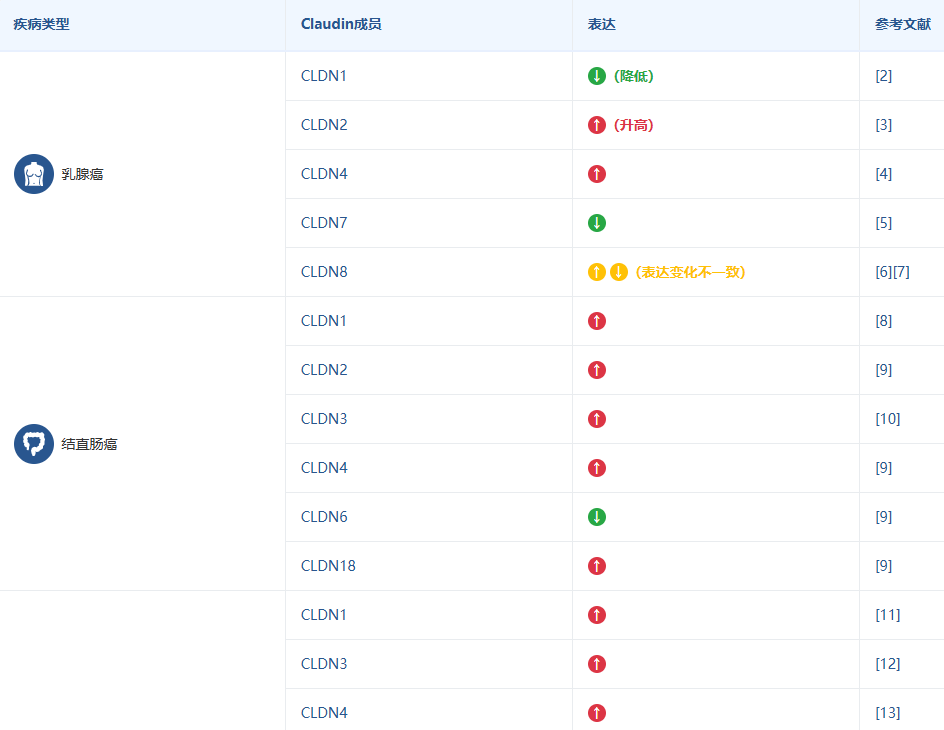
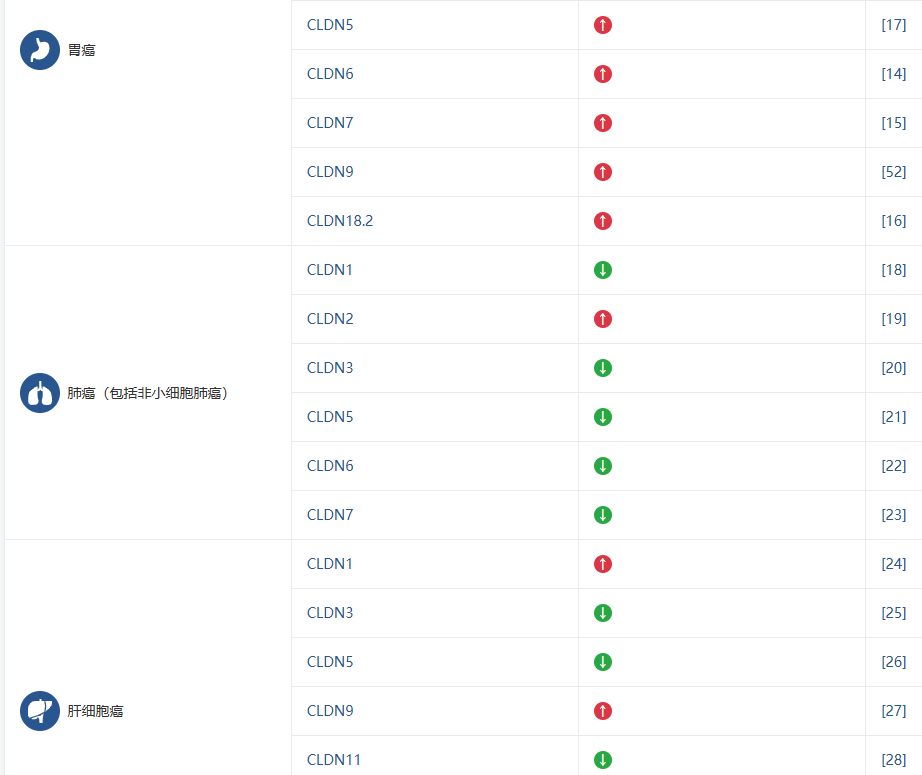
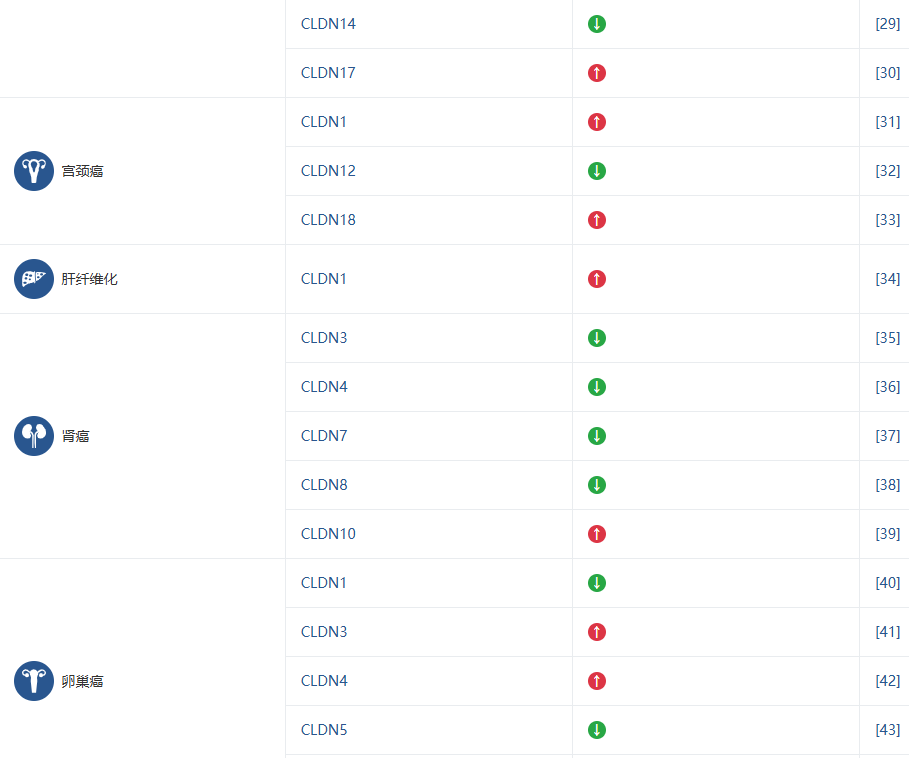
3. 研究热点与靶点聚焦
Claudin 领域正处于快速发展阶段,多个家族成员作为极具前景的治疗靶点和诊断标志物而备受关注。以下是目前活跃研究中的几个关键靶点和领域:
CLDN18.2 是一种在正常胃粘膜上皮细胞中高度特异性表达的 Claudin 蛋白,而在正常组织中表达极低。然而,它却在胃癌和胰腺癌等多种恶性肿瘤中普遍存在高表达,使其成为一个理想的肿瘤特异性靶点。这一独特的表达模式赋予了 CLDN18.2 巨大的应用潜力,尤其是在嵌合抗原受体 T 细胞(CAR-T)疗法和抗体偶联药物(ADCs)等新型癌症免疫治疗领域。
查看CLDN18.2相关产品
CLDN3作为紧密连接关键组分,不仅参与维持上皮细胞极性与屏障功能,还在调控基因转录、细胞增殖分化、代谢及免疫微环境等方面发挥多维作用。其在肿瘤中的作用复杂且高度依赖组织背景:在肝癌中通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin-EMT轴和调控胆汁酸代谢发挥抑癌作用;而在肺腺癌、结直肠癌及卵巢癌中则异常高表达,激活PI3K-Akt、ERK或JNK/AP-1等通路促进恶性进展。这种"抑癌-促癌"双重特性使其成为需精准匹配适应症的重要靶向干预节点。
查看 CLDN3相关产品
CLDN4在正常组织中表达受限,却在胰腺癌、胃癌、卵巢癌等多种恶性肿瘤中显著上调,具有高度肿瘤选择性。其参与调控细胞极性、信号传导及耐药机制,已成为热门的免疫治疗靶点。目前,靶向CLDN4的双抗药物ASP-1002已进入临床开发阶段,展现出良好的安全性和初步疗效,有望填补难治性实体瘤的治疗空白。
查看CLDN4相关产品
CLDN6在成人正常组织中几乎不表达,但在多种癌症(如睾丸癌、子宫内膜癌、肺癌)中重新激活,具备理想肿瘤特异性抗原特征。因其在"免疫冷肿瘤"中的高表达,CLDN6成为激活抗肿瘤免疫应答的重要突破口。ADC、CAR-T细胞疗法及双特异性抗体等前沿技术正加速推进CLDN6靶向治疗,多项临床管线已展现初步疗效。
查看 CLDN6相关产品
CLDN9是紧密连接蛋白家族中研究较少但极具潜力的成员。近期研究发现,CLDN9在胃癌组织中呈现特异性高表达,且与肿瘤侵袭性增强及不良预后显著相关。其在正常组织中表达受限,赋予其良好的治疗窗口。随着对其在胃癌发生发展中作用机制的逐步揭示,CLDN9正成为抗体类药物差异化布局的新方向,有望为胃癌精准治疗提供全新选择。
查看CLDN9相关产品
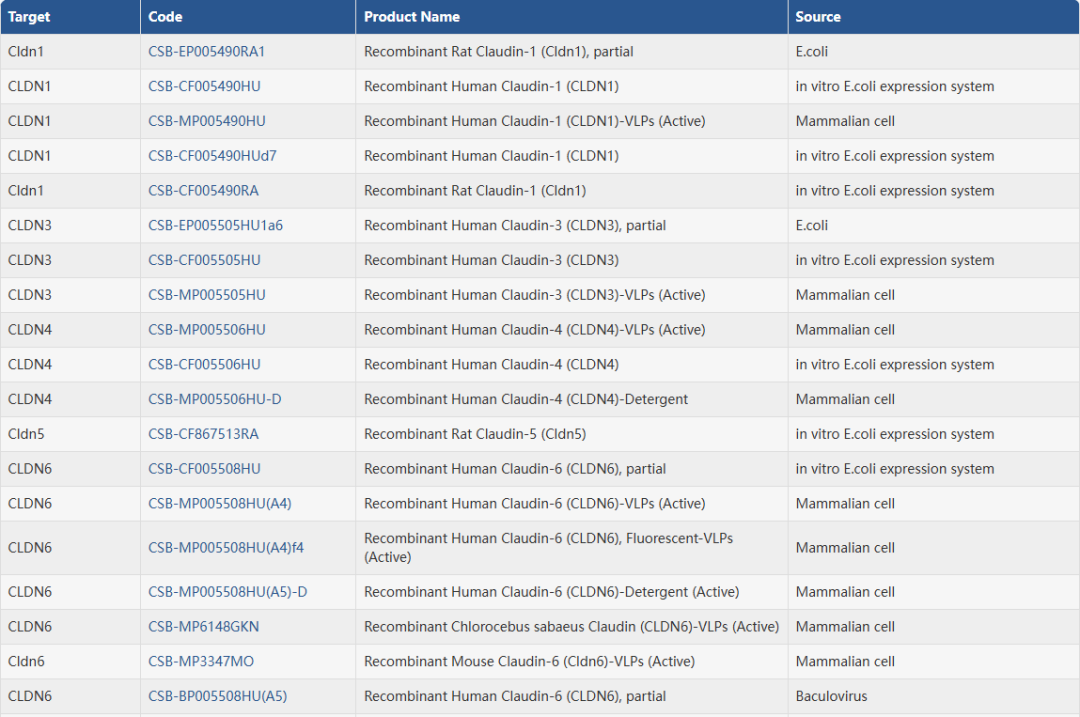
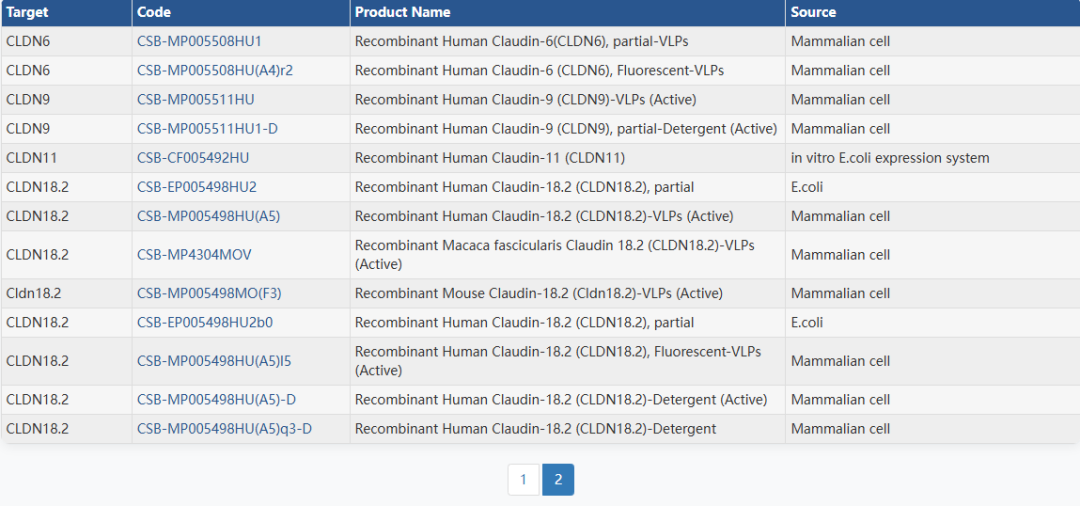
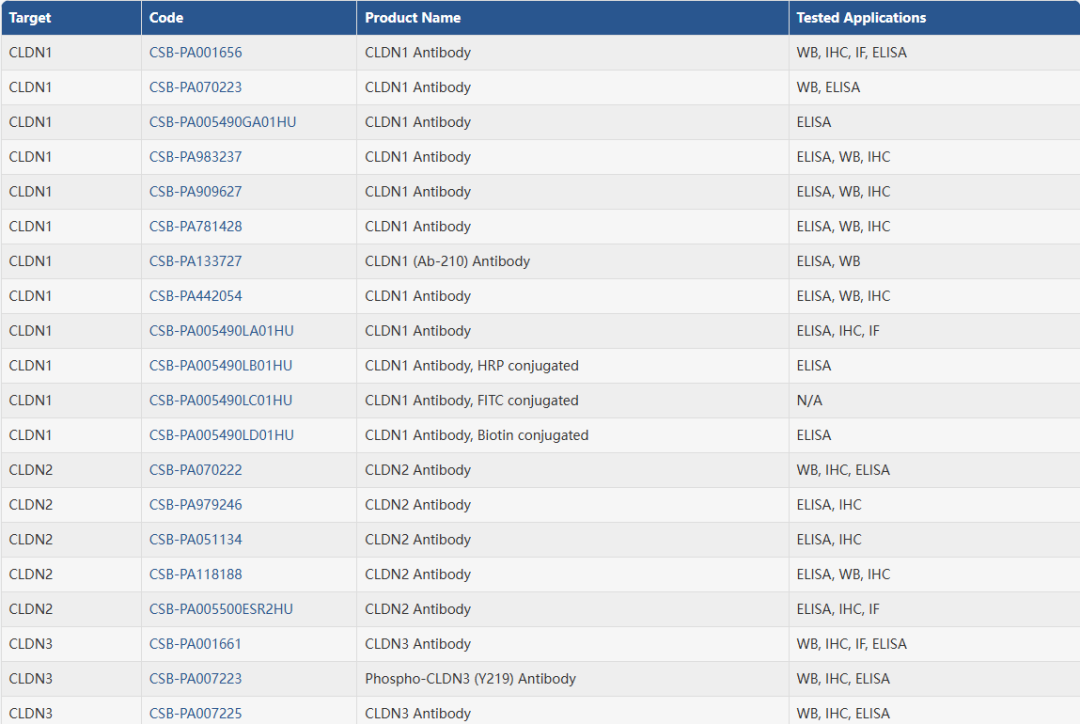
4. 华美生物Claudin全系列产品
华美生物提供覆盖 27种Claudin家族成员的完整科研工具,包括高纯度重组蛋白、经多平台验证的抗体以及高灵敏度ELISA试剂盒,助力从基础机制到转化应用的全链条研究。无论您聚焦 CLDN18.2、CLDN6 等热门靶点,还是探索其他 Claudin 成员的生物学功能,我们都为您准备了可靠、高效的实验解决方案。
重组蛋白
抗体
ELISA试剂盒
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
参考文献:
[1] Bao L,Yang S,Yang S, et al. Exploring claudin proteins: from sequence motifs to their impact on tight junction-mediated signaling pathways. Amino Acids. 2025;57 (1):48.
[2] Ma F,Zheng S,Ding X, et al. A CLDN1-negative phenotype predicts poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9 (11):e112765.
[3] Kimbung S,Kovács A,Fernö M, et al. Claudin-2 is an independent negative prognostic factor in breast cancer and specifically predicts early liver recurrences. Mol Oncol. 2014;8 (1):119-28.
[4] Gao Y,Tang L,Ning K, et al. A novel PAK4-CEBPB-CLDN4 axis involving in breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;511 (2):404-408.
[5] West JJ,Golloshi R,Cho CY, et al. Claudin 7 suppresses invasion and metastasis through repression of a smooth muscle actin program. J Cell Biol. 2024;223 (12):.
[6] Lou Y,Jiang WG,Ji W, et al. Knockdown of Claudin-8 (CLDN8) Indicates a Link Between Breast Cancer Cell Sensitivity to Chemotherapeutics and Reveals a Potential Use of CLDN8 as a Molecular Diagnostic and Target for Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26 (11):.
[7] Zhang Y,Zheng A,Jin Z, et al. The Expression and Prognostic Significance of Claudin-8 and Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:3437-3448.
[8] Garambois V,Andrade AF,Fauvre A, et al. Improving the response to oxaliplatin by targeting chemotherapy-induced CLDN1 in resistant metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Cell Biosci. 2023;13 (1):72.
[9] Cox KE,Liu S,Hoffman RM, et al. The Expression of the Claudin Family of Proteins in Colorectal Cancer. Biomolecules. 2024;14 (3):.
[10] Andrade-Da-Costa J,De Souza WF,Boroni M, et al. N‑glycosylation and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling affect claudin‑3 levels in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2020;44 (4):1649-1661.
[11] Tannæs TM,Blom GP,Bukholm IR, et al. Up-regulation of CLDN1 in gastric cancer is correlated with reduced survival. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:586.
[12] Danilova NV,Anikina KA,Oleynikova NA, et al. [Claudin-3 expression in gastric cancer]. Arkh Patol. 2020;82 (2):5-11.
[13] Kim WS,Joo MK,Yoo AY, et al. High Expression of Claudin-4 Is Associated with Synchronous Tumors in Patients with Early Gastric Cancer. J Clin Med. 2022;11 (12):.
[14] Yu S,Zhang Y,Zhao G, et al. CLDN6 promotes tumor progression through the YAP1-snail1 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10 (12):949.
[15] Song Y,Zhao J,Sun J, et al. Claudin-7 (CLDN7) is overexpressed in gastric cancer and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, invasion and maintains mesenchymal state. Neoplasma. 2018;65 (3):349-359.
[16] Ruan DY,Luo SX,Dang Q, et al. The antibody-drug conjugate SHR-A1904 for targeting CLDN18.2 in advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a phase 1 trial. Nat Med. 2025;31 (9):3037-3046.
[17] Han L,Huang B,Chen SJ, et al. CLDN5 identified as a biomarker for metastasis and immune infiltration in gastric cancer via pan-cancer analysis. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15 (11):5032-5051.
[18] Wu YY,Tung CH,Tsai YT, et al. DNA methylation maintains the CLDN1-EPHB6-SLUG axis to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy and inhibit lung cancer progression. Theranostics. 2020;10 (19):8903-8923.
[19] Yoshino Y,Ikari A. [Cancer Malignancy by Abnormal Claudin Expression]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2024;51 (11):1100-1104.
[20] Reck M,Hantzsch-Kuhn B,Olchers T, et al. Reduced Claudin-3 Expression Is Linked to Unfavorable Tumor Features and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2026;17:1-10.
[21] Kudinov AE,Nikonova AS,Beck TN, et al. Musashi-2 (MSI2) supports TGF-β signaling and inhibits claudins to promote non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113 (25):6955-60.
[22] Guo H,Li J,Dong Y, et al. CLDN6 inhibited cellular biological function of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells through suppressing aerobic glycolysis via the RIP1/ASK1/JNK axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024;38 (3):e23682.
[23] Xia P,Wang W,Bai Y. Claudin-7 suppresses the cytotoxicity of TRAIL-expressing mesenchymal stem cells in H460 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis. 2014;19 (3):491-505.
[24] Muller M,Jühling F,Del Zompo F, et al. Treatment of HCC with claudin-1-specific antibodies suppresses carcinogenic signaling and reprograms the tumor microenvironment. J Hepatol. 2023;78 (2):343-355.
[25] Jiang L,Yang YD,Fu L, et al. CLDN3 inhibits cancer aggressiveness via Wnt-EMT signaling and is a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5 (17):7663-76. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2288
[26] Sakaguchi T,Suzuki S,Higashi H, et al. Expression of tight junction protein claudin-5 in tumor vessels and sinusoidal endothelium in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2008;147 (1):123-31.
[27] Liu H,Wang M,Liang N, et al. Claudin-9 enhances the metastatic potential of hepatocytes via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019;30 (8):722-731.
[28] Yang J,Liu X,Yuan X, et al. miR-99b promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of claudin 11 expression and may serve as a prognostic marker. Oncol Rep. 2015;34 (3):1415-23.
[29] Li CP,Cai MY,Jiang LJ, et al. CLDN14 is epigenetically silenced by EZH2-mediated H3K27ME3 and is a novel prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2016;37 (6):557-566.
[30] Sun L,Feng L,Cui J. Increased expression of claudin-17 promotes a malignant phenotype in hepatocyte via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling and is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2018;13 (1):72. doi:10.1186/s13000-018-0749-1
[31] Zhang WN,Wang XL,Zhu D, et al. CLDN1 expression in cervical cancer cells is related to tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncotarget. 2016;7 (52):87449-87461.
[32] Kobayashi M,Sugimoto K,Endo Y, et al. Reduced Claudin-12 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Cervical Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22 (7).
[33] Yokawa Y,Tanaka T,Mishima R, et al. Claudin-18 expression in gastric type adenocarcinoma and HPV-associated adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix. Histopathology. 2025.
[34] Saviano A,El Saghire H,Crouchet E, et al. A monoclonal antibody targeting nonjunctional claudin-1 inhibits fibrosis in patient-derived models by modulating cell plasticity. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14 (676):eabj4221.
[35] Büyücek S,Schraps N,Chirico V, et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of Claudin-3 expression in cancer: a tissue microarray study on 14,966 tumor samples. Biomark Res. 2024;12 (1):154.
[36] Owari T,Sasaki T,Fujii K, et al. Role of Nuclear Claudin-4 in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21 (21).
[37] Li Y,Gong Y,Ning X, et al. Downregulation of CLDN7 due to promoter hypermethylation is associated with human clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and poor prognosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37 (1):276.
[38] Zhu Z,Xu C,Lin L, et al. Prognostic Value and Potential Biological Functions of CLDN8 in Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:9135-9145.
[39] Onagi A,Sugimoto K,Kobayashi M, et al. Extrajunctional CLDN10 cooperates with LAT1 and accelerates clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22 (1):588.
[40] Zhang H,Lin Y,Kang K, et al. PABPC3 drives ovarian cancer metastasis and drug sensitivity by downregulating CLDN1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2025;16 (1):840.
[41] He ZY,Wei XW,Luo M, et al. Folate-linked lipoplexes for short hairpin RNA targeting claudin-3 delivery in ovarian cancer xenografts. J Control Release. 2013;172 (3):679-89.
[42] Hu P,Lei L,Wang Y, et al. CLDN4 as a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker and Its Association with Immune Infiltrates in Ovarian Cancer. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:1075265.
[43] Herr D,Sallmann A,Bekes I, et al. VEGF induces ascites in ovarian cancer patients via increasing peritoneal permeability by downregulation of Claudin 5. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;127 (1):210-6.
[44] Dahiya N,Becker KG,Wood WH, et al. Claudin-7 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer and promotes invasion. PLoS One. 2011;6 (7):e22119.
[45] Martínez-Camberos A,Alvarez-Arrazola M,Arámbula-Meraz E, et al. Dysregulation of KRT19, TIMP1, and CLDN1 gene expression is associated with thyroid cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;617 (Pt 1):55-59.
[46] Zhu L,Tang N,Hang H, et al. Loss of Claudin-1 incurred by DNMT aberration promotes pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2024;586:216611.
[47] Bang C,Park MG,Cho IK, et al. Liposomes targeting the cancer cell-exposed receptor, claudin-4, for pancreatic cancer chemotherapy. Biomater Res. 2023;27 (1):53.
[48] Tojjari A,Idrissi YA,Saeed A. Emerging targets in gastric and pancreatic cancer: Focus on claudin 18.2. Cancer Lett. 2024;611:217362.
[49] Büscheck F,Höflmayer D,Hube-Magg C, et al. Claudin-1 upregulation is associated with favorable tumor features and a reduced risk for biochemical recurrence in ERG-positive prostate cancer. World J Urol. 2020;38 (9):2185-2196.
[50] Maeda T,Murata M,Chiba H, et al. Claudin-4-targeted therapy using Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin for prostate cancer. Prostate. 2012;72 (4):351-60.
[51] Coutinho-Camillo CM,Lourenço SV,da Fonseca FP, et al. Claudin expression is dysregulated in prostate adenocarcinomas but does not correlate with main clinicopathological parameters. Pathology. 2011;43 (2):143-8.
[52] Hu Q,Han L,Wang J, et al. CLDN9 and hsa-miR-4496 as non-invasive biomarkers for gastric cancer detection. Discov Oncol. 2025;16 (1):486.



