武汉华美生物工程有限公司CUSABIO®品牌商
15 年
手机商铺
- NaN
- 0
- 0
- 2
- 2
推荐产品
公司新闻/正文
肿瘤免疫治疗生力军——PD1抑制剂的研究和应用现状
1283 人阅读发布时间:2021-11-05 09:43

近些年,肿瘤免疫治疗已经在临床取得了非常显著的进展,比如过继细胞转移疗法(Adoptive cell transfer therapy)以及免 疫 检 查 点 封 锁 疗 法 ( Immune checkpoint blockade,ICB)。2018年,靶向细胞程序性死亡/程序性死亡配体( Programmed Cell Death 1/Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1,PD1/PDL1)通路的ICB获得了诺贝尔生理学或医学奖。这极大地鼓舞了从事肿瘤免疫疗法的研究者的信心。如今,靶向PD1/PDL1的ICB已被批准应用于多种实体肿瘤的临床治疗。

当T细胞面对MHCs上的同一抗原时,会释放IFN-γ,从而提高肿瘤杀伤率。CD8+T细胞释放IFN-γ上调肿瘤细胞和间质细胞上PDL1的表达 [4,5]。与此同时,TCR信号通过上调T细胞表面的PD1表达对肿瘤免疫过程进行负调控,削弱T细胞的抗肿瘤功能 [6-8]。因此,针对PD1和PDL1相互作用的免疫治疗可以激活因PD1/PDL1信号抑制而失活的T细胞。现有的研究已经证明,PD1/PDL1阻断剂对黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌、肾细胞癌、头颈部鳞状细胞癌、尿路上皮癌等实体瘤有显著作用,并且还有更多的实体瘤正在被验证当中。(图1 [9])
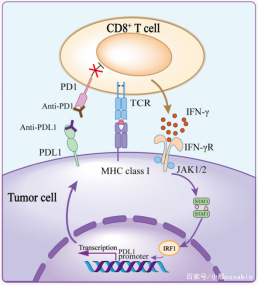
图1
*图片来源于Front Cell Dev Biol出版物[9]
(a)高突变肿瘤更容易产生新的肿瘤抗原,减少抗原免疫原性,诱导肿瘤排斥反应;
(b)B2M突变导致肿瘤抗原递呈失败;
(c)原发性JAK1/2基因突变导致癌细胞对IFN-γ信号抵抗,抑制PD1/PDL1非依赖途径的T细胞反应;
(d)肿瘤浸润的T细胞中,除PD1/PDL1外其他免疫检查点也被上调,仅抑制PD1/PDL1不足以挽救T细胞耗竭;
(e)TME中含有多种免疫抑制细胞,抑制T细胞活性和对PD1抑制剂的响应;
(f)癌基因突变和异常激活引起的抗肿瘤免疫抑制。(图2[9])
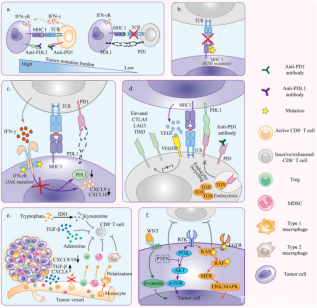
图2
*图片来源于Front Cell Dev Biol出版物[9]
抗PD1/PDL1治疗中,获得性耐药很有可能来源与宿主免疫系统,其机制主要是:
(a)在PD1/PDL1抑制剂的筛选压力下,免疫编辑选择性的保留了具有抗肿瘤优势的肿瘤细胞;
(b)抗PD1/PDL1治疗过程中,代偿抑制信号表达增加,使CD8+T细胞难以激活;
(c)肿瘤特异性T细胞如果没有分化为记忆T细胞,治疗反应无法持续,特异T细胞耗竭也将导致宿主耐药。(图3 [9])

随着免疫治疗的不断发展,针对肿瘤免疫逃逸的不同机制提出相应的解决策略是目前的研究方向之一。目前应对肿瘤免疫逃逸的策略主要集中在加强T细胞启动、逆转T细胞耗竭、增加T细胞浸润和改善免疫抑制微环境等几个方面。(表1 [9])

随着PD1/PDL1阻断剂不断进入临床应用,抗PD1/PDL1疗法已成为肿瘤免疫治疗的里程碑。尽管该疗法在实体瘤的治疗中显示出令人惊叹的疗效,但其耐药性的频发也使该疗法的推广过程不尽人意。因此,对PD1/PDL1阻断剂耐药机制的实验室及临床前研究对于制定克服策略至关重要,其研究过程中所需的生物制剂、药品、科研服务都是必不可少的基石。
[1] Chen DS, Mellman I: Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39(1):1-10.
[2] Maimela NR, Liu S, Zhang Y: Fatesof CD8+ T cells in Tumor Microenvironment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2019, 17:1-13.
[3] Pardoll D: Cancer and the Immune System: Basic Concepts and Targets for Intervention. Semin Oncol 2015, 42(4):523-538.
[4] Ribas A: Adaptive Immune Resistance: How Cancer Protects from Immune Attack. Cancer Discov 2015, 5(9):915-919.
[5] Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Moreno BH, Saco J, Escuin-Ordinas H, Rodriguez GA, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Hugo W, Wang Xet al: Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep 2017, 19(6):1189-1201.
[6] Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H, Honjo T:Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol 1996, 8(5):765-772.
[7] Akinleye A, Rasool Z: Immune checkpoint inhibitors of PD-L1 as cancer therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol 2019, 12(1):92.
[8] Ribas A, Wolchok JD: Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade.Science 2018, 359(6382):1350-1355.
[9] Lei Q, Wang D, Sun K, Wang L, Zhang Y: Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-PD1/PDL1 Therapy in Solid Tumors. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8:672.
[10] Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA, Ribas A: Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168(4):707-723.
华美CUSABIO提供优质PD-L1相关科研产品助力您的研究!
Recombinant Human CD274, partial (Active) (CSB-MP878942HU1)
PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody(CSB-MA878942A0m)
PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody(CSB-MA878942A1m)
Human CD274 ELISA Kit(CSB-E13644h)
Mouse CD274 ELISA kit(CSB-EL004911MO)

PD-L1重组蛋白(活性验证)
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1(CD274),partial (Active)(CSB-MP878942HU1)
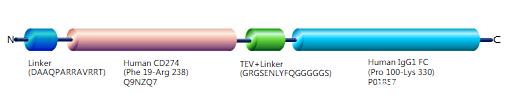
来源:Mammalian cell
标签:C-terminal hFc-tagged
纯度:Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
表达区域:19-238aa
分子结构:
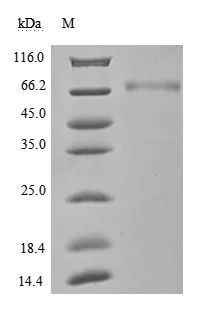
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
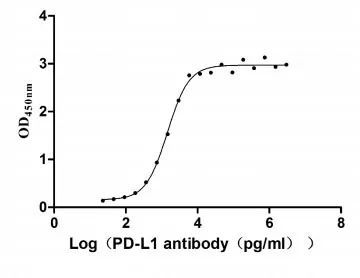
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized PD-L1 at 2 μg/ml can bind Anti- PD-L1 mouse monoclonal antibody(CSB-MA878942A1m,antigen from E.coli), the EC50 of human PD-L1 protein is 1.252-1.653 ng/mL.
PD-L1 抗体产品
PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody( CSB-MA878942A0m)
免疫原:
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 protein (19-238AA)
反应种属:Human
应用范围:ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
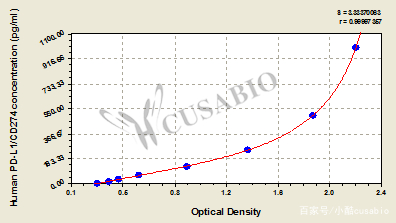
PD-L1 ELISA Kit产品
Human PD-L1 ELISA kit (CSB-E13644h)
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates
检测范围:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
灵敏度: 3.9 pg/mL
引用文献
Rastvorljivi programirani smrtni ligand 1 (sPD-L1) i programirani smrtni ligand 1 (sPD-1) kao potencijalni biomarkeri za dijagnozu i prognozu kod pacijenata sa gliomom S Liu,Journal of Medical Biochemistry,2020
The Clinical Significance of Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 in Lung Cancer Taher Abu Hejleh, et al,Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology,2019
Matrix metalloproteinase and cytokine profiles from cell co-cultures and their role in oral inflammation and head and neck cancer Amber Marie Bates.et al,/,2018
SCCA, TSGF, and the Long Non-Coding RNA AC007271.3 are Effective Biomarkers for Diagnosing Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Shao T.et al,Cell Physiol Biochem,2018
药靶蛋白服务手册免费下载,
关注“武汉华美生物”官方微信,后台回复:“药靶蛋白”
—END—
——华美生物·让科研变得有温度!——



